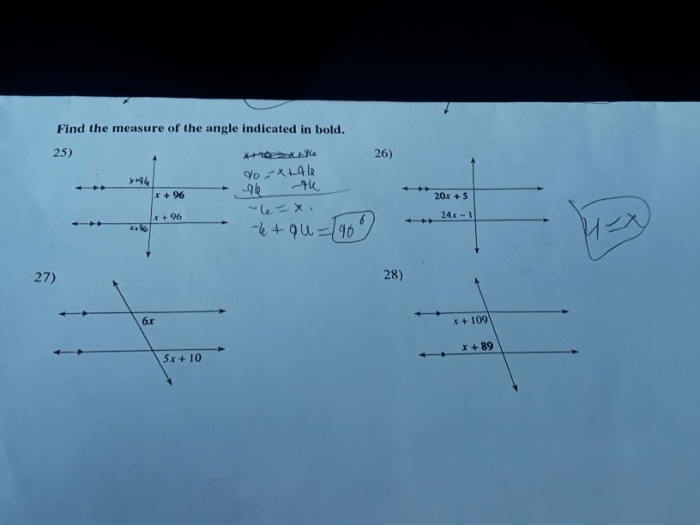
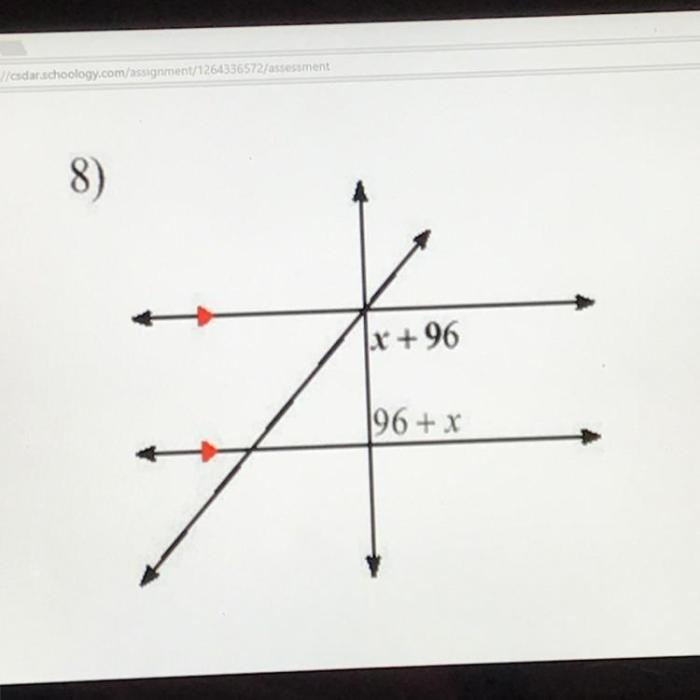
Find the measure of the angle indicated in bold answers, a topic that captivates the imagination and sparks intellectual curiosity, sets the stage for this enthralling narrative. Join us on an exploration of angles, their measurement, and the fascinating relationships that define them, presented in a gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif that illuminates the subject with clarity and precision.
From the fundamental concepts of angle measurement to the intricate properties of angle bisectors, this comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of angles, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to conquer any angle-related challenge. Prepare to embark on a journey of geometric discovery, where angles take center stage and their secrets are laid bare.
Angle Measurement: Find The Measure Of The Angle Indicated In Bold Answers

Angle measurement is a fundamental concept in geometry. It involves determining the size of an angle, which is formed by the intersection of two rays or lines. Understanding angle measurement is crucial for various applications, including architecture, engineering, and trigonometry.
To measure an angle, a protractor is commonly used. A protractor is a semicircular tool with a scale marked in degrees. To use a protractor, align its center with the vertex of the angle and the baseline with one of the rays.
Read the scale at the point where the other ray intersects the protractor to obtain the angle measure.
Accurate angle measurement requires careful placement of the protractor and precise reading of the scale. To ensure accuracy, place the protractor firmly against the vertex and hold it steady. Read the scale perpendicularly to avoid parallax errors. Additionally, use a sharp pencil to mark the intersection points clearly.
Angle Types
Angles are classified into different types based on their measure:
- Acute angle:An angle less than 90 degrees.
- Right angle:An angle measuring exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse angle:An angle greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
- Straight angle:An angle measuring exactly 180 degrees.
- Reflex angle:An angle greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
Each angle type has distinct characteristics and applications in geometry and real-world scenarios.
Angle Relationships, Find the measure of the angle indicated in bold answers
Angles formed by intersecting lines or rays have specific relationships:
- Adjacent angles:Two angles that share a common side and a common vertex.
- Vertical angles:Two angles formed by two intersecting lines that are opposite to each other.
- Complementary angles:Two angles whose sum is 90 degrees.
- Supplementary angles:Two angles whose sum is 180 degrees.
Understanding these relationships is essential for solving angle problems and making geometric constructions.
Angle Bisectors
An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two equal parts:
- Definition:A line or ray that passes through the vertex of an angle and divides it into two equal angles.
- Construction:To construct an angle bisector using a compass and straightedge, place the compass point at the vertex and draw an arc intersecting both rays of the angle. Repeat this process from the other side of the vertex. The intersection of the two arcs forms the angle bisector.
- Properties:Angle bisectors have several important properties, including dividing the angle into two equal parts and forming perpendicular lines to the sides of the angle.
Angle bisectors play a crucial role in geometry, particularly in constructing perpendicular lines and bisecting line segments.
Angle Measurement in Triangles
Triangles have specific properties related to angle measurement:
- Triangle angle sum theorem:The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Exterior angle theorem:The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two opposite interior angles.
- Angle relationships:The angles of a triangle can be classified as acute, obtuse, or right angles, and their relationships can be used to solve triangle problems.
Understanding angle measurement in triangles is fundamental for solving geometric problems and analyzing triangle properties.
Angle Measurement in Circles
Angles can also be formed by arcs and chords in a circle:
- Central angle:An angle formed by two radii of a circle that meet at the center.
- Inscribed angle:An angle formed by two chords that intersect inside the circle.
- Angle formed by chords:An angle formed by two chords that intersect outside the circle.
Angle measurement in circles involves understanding the relationships between angles, arcs, and chords, which are crucial for solving geometric problems and analyzing circular properties.
Helpful Answers
What is the most accurate method for measuring angles?
Using a digital protractor provides the highest level of accuracy for angle measurement.
How can I determine the type of an angle without using a protractor?
Examine the angle and estimate its size. If it appears to be less than 90 degrees, it is likely an acute angle. If it appears to be greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees, it is likely an obtuse angle.
If it appears to be exactly 90 degrees, it is a right angle. If it appears to be greater than 180 degrees, it is likely a reflex angle.
What is the relationship between adjacent angles?
Adjacent angles are two angles that share a common vertex and a common side. The sum of the measures of adjacent angles is equal to 180 degrees.