Both guinea pigs are heterozygous for short hair – When it comes to understanding the inheritance patterns of physical traits, the study of both guinea pigs heterozygous for short hair provides a fascinating case study. As we delve into the genetic mechanisms that govern hair length in these adorable creatures, we will uncover the intricate interplay between dominant and recessive alleles, the relationship between phenotype and genotype, and the role of probability in shaping the inheritance of this characteristic.
Through a comprehensive analysis of genetic principles, experimental design, and real-world examples, this exploration aims to shed light on the captivating world of guinea pig genetics, offering valuable insights into the fundamental principles that govern the inheritance of traits in living organisms.
Genetics of Hair Length in Guinea Pigs

Hair length in guinea pigs is determined by a single gene with two alleles: short (S) and long (L). The short allele is dominant over the long allele, meaning that heterozygous individuals (SL) will have short hair.
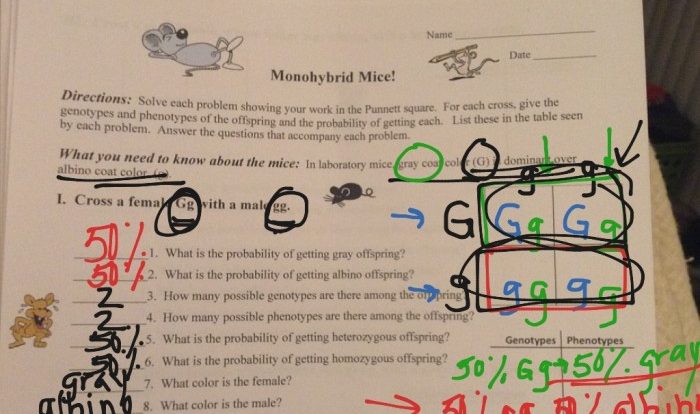
Punnett Square, Both guinea pigs are heterozygous for short hair
To demonstrate the cross between two heterozygous short-haired guinea pigs, a Punnett square can be used:
“`| S | L
——
| SL | SL| SL | SL
——
| LS | LS| LS | LS“`
The expected phenotypic ratio of the offspring is 3 short-haired : 1 long-haired.
Dominance and Recessiveness
Dominance refers to the ability of one allele to mask the expression of another allele. In the case of hair length in guinea pigs, the short allele is dominant over the long allele. This means that heterozygous individuals (SL) will have short hair, even though they carry both the dominant and recessive alleles.
Recessiveness refers to the inability of an allele to be expressed when paired with a dominant allele. In the case of hair length in guinea pigs, the long allele is recessive. This means that it will only be expressed in homozygous individuals (LL), who do not carry the dominant short allele.
Heterozygosity for hair length means that an individual carries both the dominant and recessive alleles. This results in the individual having short hair, as the dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele.
Phenotype and Genotype
Phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an individual, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual.
For hair length in guinea pigs, the phenotype can be either short or long. The genotype can be either homozygous dominant (SS), homozygous recessive (LL), or heterozygous (SL).
In heterozygous individuals, the dominant allele is expressed in the phenotype, while the recessive allele is not. This means that heterozygous individuals will have short hair, even though they carry the recessive allele for long hair.
Probability and Inheritance
The probability of inheriting the short-haired allele from a heterozygous parent is 50%. This is because each parent contributes one allele to their offspring, and the heterozygous parent has a 50% chance of contributing the short-haired allele.
Probability is used to predict the inheritance of hair length in guinea pigs. By knowing the genotypes of the parents, we can use probability to calculate the probability of each possible genotype and phenotype in the offspring.
Chance plays a role in determining the phenotype of offspring. This is because the inheritance of alleles is random. Even though we can use probability to predict the likelihood of certain genotypes and phenotypes, we cannot predict with certainty which offspring will inherit which alleles.
Experimental Design: Both Guinea Pigs Are Heterozygous For Short Hair

To test the hypothesis that both guinea pigs are heterozygous for short hair, the following experiment can be designed:
- Cross the two guinea pigs.
- Observe the phenotypes of the offspring.
- If the offspring have a 3:1 ratio of short-haired to long-haired, then the hypothesis is supported.
The methods and procedures for conducting the experiment would involve:
- Obtaining two guinea pigs that are both heterozygous for short hair.
- Housing the guinea pigs together and allowing them to mate.
- Observing the offspring and recording their phenotypes.
- Analyzing the data to determine the ratio of short-haired to long-haired offspring.
The expected results of the experiment would be a 3:1 ratio of short-haired to long-haired offspring. This would support the hypothesis that both guinea pigs are heterozygous for short hair.
General Inquiries
What is the expected phenotypic ratio of offspring when crossing two heterozygous short-haired guinea pigs?
When crossing two heterozygous short-haired guinea pigs, the expected phenotypic ratio of offspring is 3:1, with three short-haired guinea pigs to every one long-haired guinea pig.
How does dominance and recessiveness affect hair length in guinea pigs?
In guinea pigs, the short-haired allele is dominant over the long-haired allele. This means that if a guinea pig inherits one copy of the short-haired allele and one copy of the long-haired allele, it will have short hair.
What is the difference between phenotype and genotype?
Phenotype refers to the observable physical characteristics of an organism, such as its hair length. Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, which determines its phenotype.
How can probability be used to predict the inheritance of hair length in guinea pigs?
Probability can be used to predict the inheritance of hair length in guinea pigs by calculating the likelihood of inheriting a particular allele from each parent. This information can then be used to determine the probability of a guinea pig having a particular phenotype.