Operant conditioning punishment and schedules of reinforcement worksheet answers – Embark on an exploration of operant conditioning punishment and schedules of reinforcement, unraveling their intricacies and practical applications through the lens of this comprehensive worksheet. Delve into the mechanisms of punishment, the nuances of reinforcement schedules, and their profound impact on behavior modification.
This guide empowers you with the knowledge and tools to effectively navigate the complexities of operant conditioning.
Uncover the theoretical underpinnings of operant conditioning punishment, examining both positive and negative reinforcement techniques. Discover the potential drawbacks associated with punishment and delve into the various schedules of reinforcement, including continuous, intermittent, fixed, and variable. Explore how each schedule influences the rate and pattern of responding, weighing their advantages and disadvantages.
Operant Conditioning Punishment: Operant Conditioning Punishment And Schedules Of Reinforcement Worksheet Answers
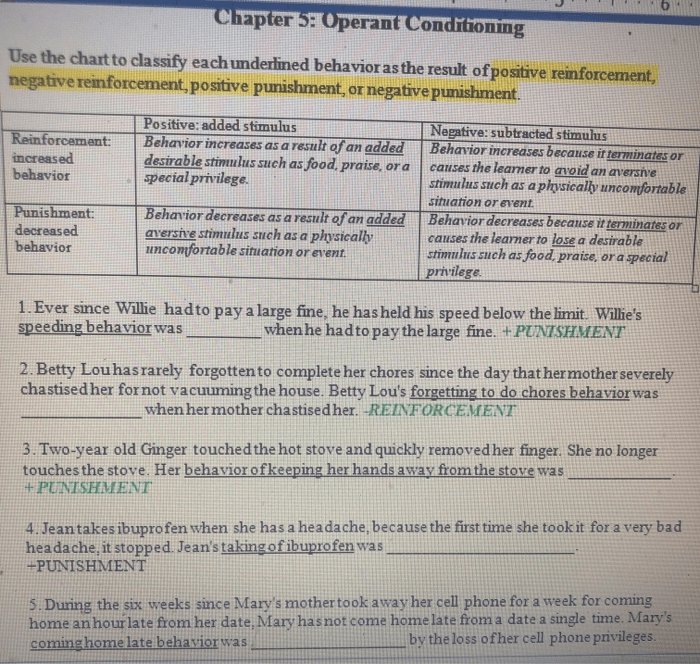
Operant conditioning punishment involves decreasing the likelihood of a behavior by delivering an aversive consequence after the behavior occurs.
Positive Punishment
Positive punishment involves adding an aversive stimulus after a behavior, such as:
- Giving a child a timeout after they hit their sibling
- Fining a driver for speeding
Negative Punishment
Negative punishment involves removing a positive stimulus after a behavior, such as:
- Taking away a child’s favorite toy after they misbehave
- Revoking a driver’s license after repeated traffic violations
Drawbacks of Punishment
While punishment can be effective in suppressing behavior, it has potential drawbacks:
- Can lead to fear and aggression
- May not address the underlying causes of the behavior
- Can damage the relationship between the punisher and the punished
Schedules of Reinforcement
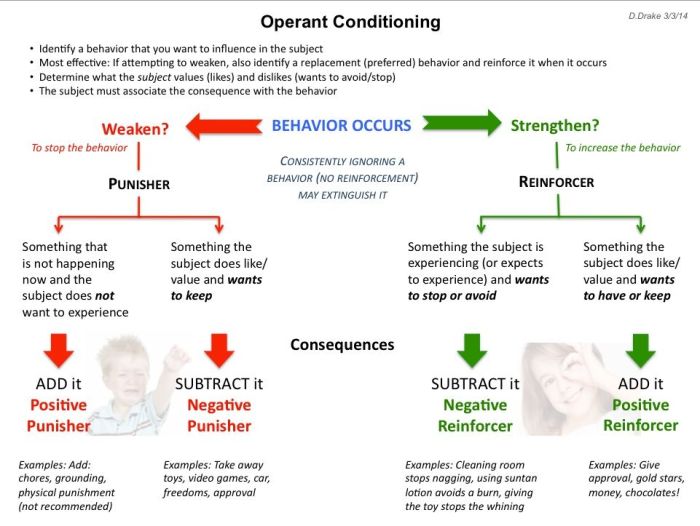
Schedules of reinforcement determine how often a behavior is reinforced.
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcement is delivered every time the desired behavior occurs. This leads to a rapid increase in the rate of responding, but extinction occurs quickly when reinforcement stops.
Intermittent Reinforcement, Operant conditioning punishment and schedules of reinforcement worksheet answers
Reinforcement is not delivered every time the behavior occurs. This leads to a slower increase in the rate of responding, but extinction occurs more slowly.
Fixed Schedules
The reinforcement is delivered after a set number of responses or at a set time interval.
- Fixed-ratio schedule: Reinforcement is delivered after a set number of responses (e.g., every fifth response)
- Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforcement is delivered after a set amount of time (e.g., every 10 minutes)
Variable Schedules
The reinforcement is delivered after a varying number of responses or at varying time intervals.
- Variable-ratio schedule: Reinforcement is delivered after a varying number of responses (e.g., sometimes after 5 responses, sometimes after 10)
- Variable-interval schedule: Reinforcement is delivered after a varying amount of time (e.g., sometimes after 5 minutes, sometimes after 15)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Schedules
Continuous Reinforcement
- Advantages: Rapid acquisition of behavior
- Disadvantages: Extinction occurs quickly
Intermittent Reinforcement
- Advantages: Slows extinction
- Disadvantages: Slower acquisition of behavior
Fixed Schedules
- Advantages: Predictable, can lead to high rates of responding
- Disadvantages: Can lead to pausing (stopping responding) just before reinforcement is delivered
Variable Schedules
- Advantages: Slows extinction, produces a steady rate of responding
- Disadvantages: Can be unpredictable
Answers to Common Questions
What is the primary goal of operant conditioning punishment?
To decrease the frequency of a specific behavior by introducing an aversive consequence.
How does a variable-ratio schedule of reinforcement differ from a fixed-ratio schedule?
In a variable-ratio schedule, the number of responses required for reinforcement varies, while in a fixed-ratio schedule, the number remains constant.
What ethical considerations should be taken into account when using punishment in operant conditioning?
Punishment should only be used as a last resort, and its potential negative consequences must be carefully weighed against its potential benefits.
