In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to label the block diagram of the lithosphere appropriately. This undertaking will shed light on the Earth’s outermost layer, its composition, and its profound significance in plate tectonics.
The lithosphere, a rigid and dynamic component of our planet, plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface and driving geological processes. By accurately labeling its components, we gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s structure and its ever-changing nature.
Lithosphere: Label The Block Diagram Of The Lithosphere Appropriately.
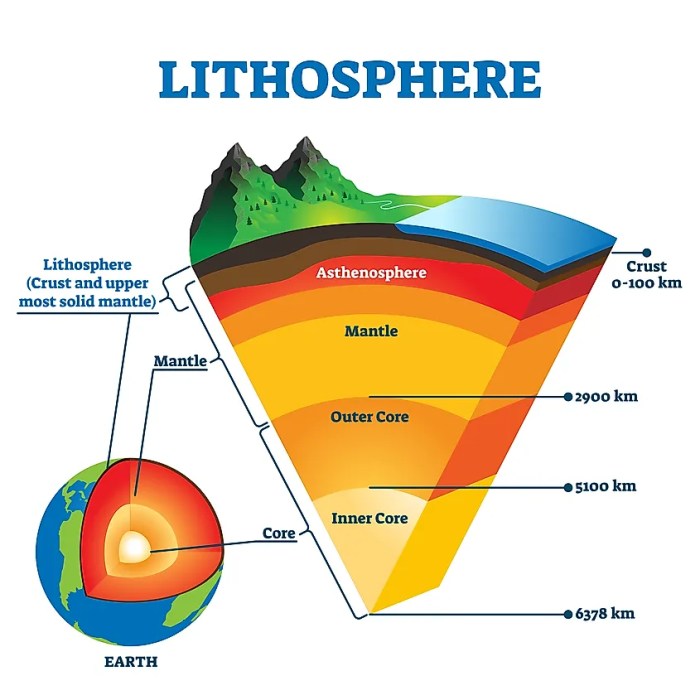
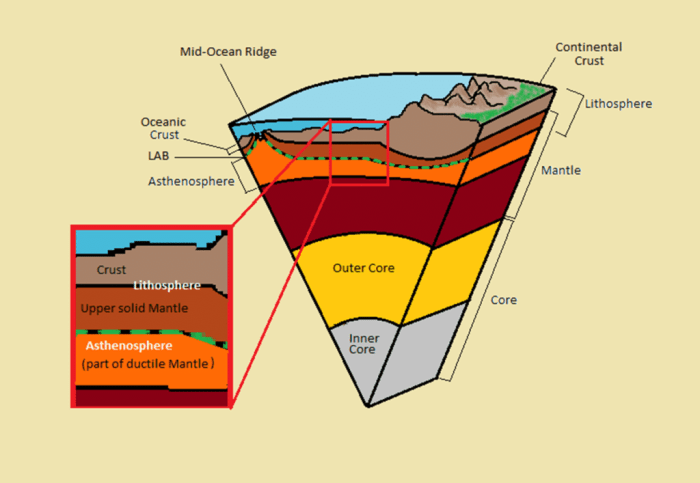
The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost layer of the Earth, composed primarily of the crust and the uppermost mantle. It is relatively thin, ranging in thickness from about 50 kilometers (31 miles) beneath the oceans to 150 kilometers (93 miles) beneath the continents.
The lithosphere is divided into two types: oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere is composed of the oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle, while continental lithosphere is composed of the continental crust and the underlying upper mantle.
Crust
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is composed of a variety of rocks. The continental crust is composed primarily of granite and other felsic rocks, while the oceanic crust is composed primarily of basalt and other mafic rocks.
The crust is relatively thin, ranging in thickness from about 5 kilometers (3 miles) beneath the oceans to 50 kilometers (31 miles) beneath the continents.
Mantle
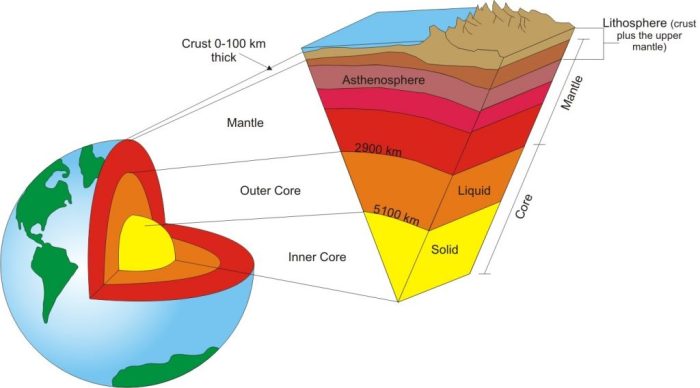
The mantle is the layer of the Earth beneath the crust and is composed primarily of peridotite, a rock composed of olivine and pyroxene. The mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) thick and is divided into two layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
The upper mantle is more rigid than the lower mantle and is composed of solid rock. The lower mantle is more fluid than the upper mantle and is composed of molten rock.
Core
The core is the innermost layer of the Earth and is composed primarily of iron and nickel. The core is about 2,200 kilometers (1,370 miles) thick and is divided into two layers: the inner core and the outer core. The inner core is solid, while the outer core is liquid.
The core is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere is the layer of the Earth beneath the lithosphere and is composed of partially molten rock. The asthenosphere is about 200 kilometers (124 miles) thick and is responsible for the movement of the lithosphere. The lithosphere is divided into a number of tectonic plates, which move across the asthenosphere.
Tectonic Plates, Label the block diagram of the lithosphere appropriately.
Tectonic plates are large pieces of the lithosphere that move across the asthenosphere. Tectonic plates are composed of both continental and oceanic lithosphere. The movement of tectonic plates is responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
Questions and Answers
What is the lithosphere?
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the uppermost mantle.
What is the significance of labeling the lithosphere?
Labeling the lithosphere helps us visualize its structure, identify its components, and understand their roles in geological processes.
How does the lithosphere interact with other layers of the Earth?
The lithosphere interacts with the underlying asthenosphere, allowing for plate movement and the formation of geological features.