Epithelial tissue and connective tissue quiz – Embark on an educational journey with our Epithelial and Connective Tissue Quiz, a meticulously crafted assessment designed to illuminate the intricacies of these fundamental tissues. Delve into their unique characteristics, functions, and the intricate interplay that defines their roles within the human body.
Epithelial tissues, the guardians of our internal and external surfaces, and connective tissues, the versatile architects of our structural framework, play pivotal roles in maintaining homeostasis and facilitating essential physiological processes. This quiz will challenge your understanding of these vital tissues, testing your knowledge and reinforcing key concepts.
Epithelial Tissue: Epithelial Tissue And Connective Tissue Quiz
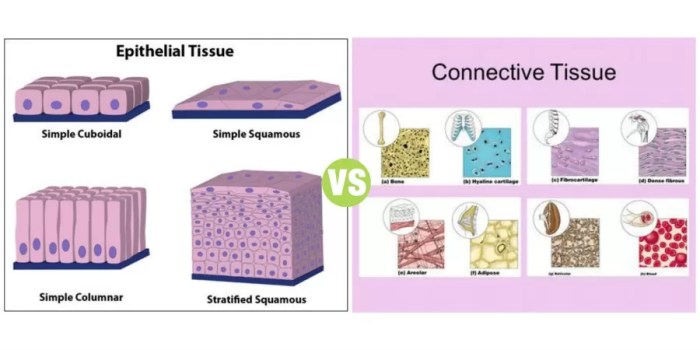
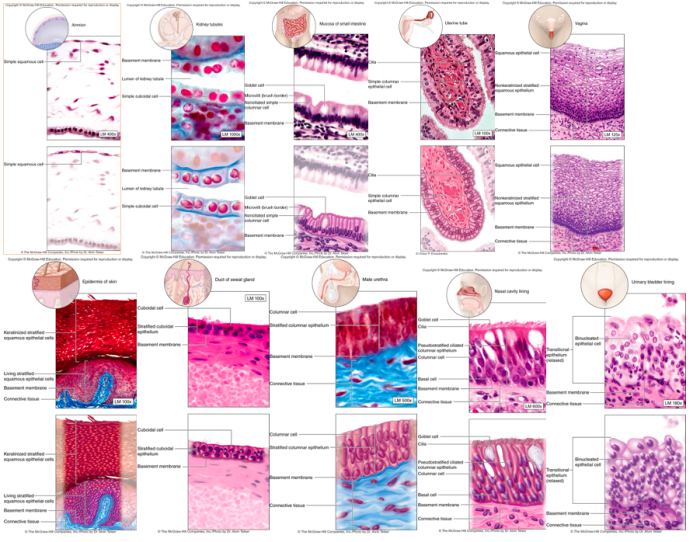
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the body’s surfaces, both internal and external. It forms the lining of organs, cavities, and blood vessels, and it protects the body from the environment. Epithelial tissue is composed of closely packed cells that are arranged in a single layer or multiple layers.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue, Epithelial tissue and connective tissue quiz
- Closely packed cells with little extracellular matrix
- Cells are arranged in a single layer or multiple layers
- Cells have a free surface that is exposed to the environment or to a body cavity
- Cells have a basal surface that is attached to a basement membrane
- Cells are polarized, meaning that they have different structures and functions at their apical and basal surfaces
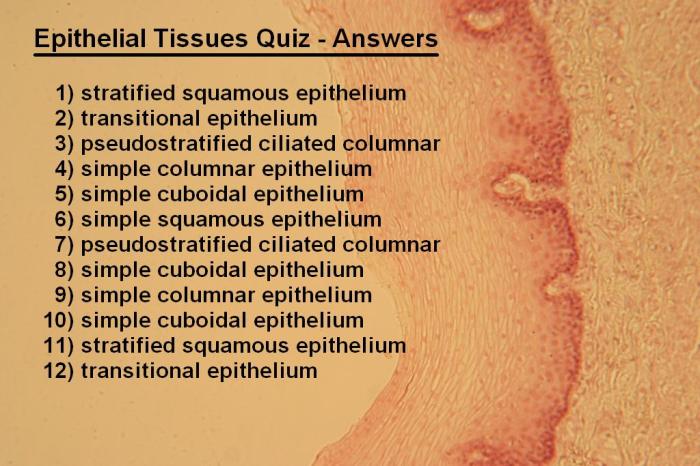
Types of Epithelial Tissue
There are many different types of epithelial tissue, each with its own unique structure and function. Some of the most common types of epithelial tissue include:
- Simple squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of flat cells. It is found in the lining of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
- Simple cuboidal epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells. It is found in the lining of glands and ducts.
- Simple columnar epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells. It is found in the lining of the digestive tract and respiratory tract.
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: This type of epithelium appears to be stratified, but it is actually composed of a single layer of cells. The cells are tall and column-shaped, and they have nuclei that are located at different levels. It is found in the lining of the trachea and bronchi.
- Stratified squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells. The cells in the superficial layers are flat, while the cells in the deeper layers are cuboidal or columnar. It is found in the lining of the skin and esophagus.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue performs a variety of important functions, including:
- Protection: Epithelial tissue protects the body from the environment by forming a barrier against pathogens and other harmful substances.
- Secretion: Epithelial tissue secretes hormones, enzymes, and other substances that are necessary for the body’s function.
- Absorption: Epithelial tissue absorbs nutrients and other substances from the environment.
- Excretion: Epithelial tissue excretes waste products from the body.
Questions Often Asked
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue serves as a protective barrier, lining the surfaces of organs, cavities, and blood vessels to prevent the entry of pathogens and regulate the passage of substances.
How do connective tissues differ from epithelial tissues?
Connective tissues are characterized by their abundant extracellular matrix, which provides structural support, cushioning, and facilitates communication between cells, while epithelial tissues lack this matrix and form tightly packed layers.
What are the main types of connective tissue?
The major types of connective tissue include loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone, and blood.