The endocrine system hormones fill in handout embarks on a captivating journey into the realm of hormones, unveiling their pivotal role in regulating our bodies’ intricate functions. This comprehensive resource delves into the diverse types of endocrine glands, deciphering their intricate mechanisms of action and the delicate balance of hormone secretion.
As we navigate the depths of this endocrine odyssey, we will unravel the intricate mechanisms by which hormones exert their influence on target cells, guided by the enigmatic dance of receptors and second messengers. The intricate interplay of feedback loops, maintaining hormonal harmony, will be laid bare, illuminating the delicate equilibrium that underpins our physiological well-being.
Introduction: Endocrine System Hormones Fill In Handout
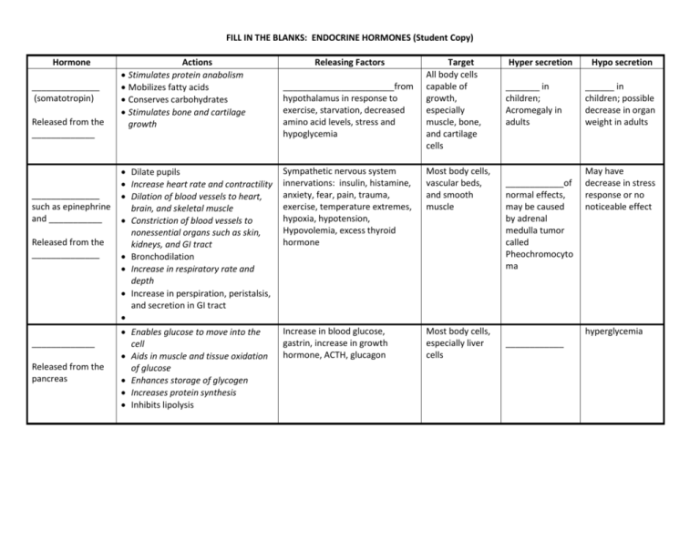
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
Types of Endocrine Glands
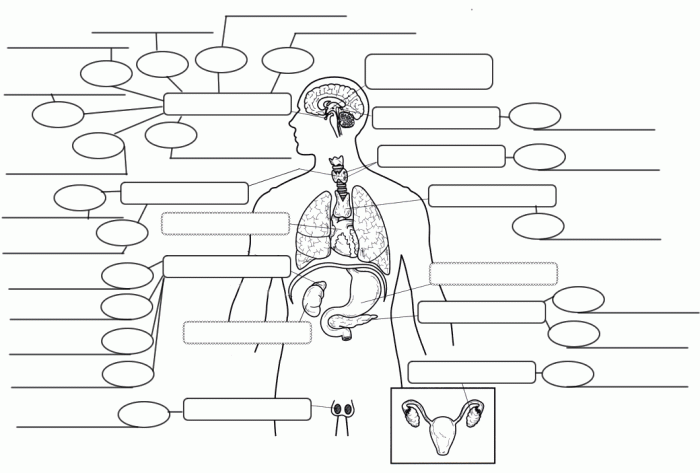
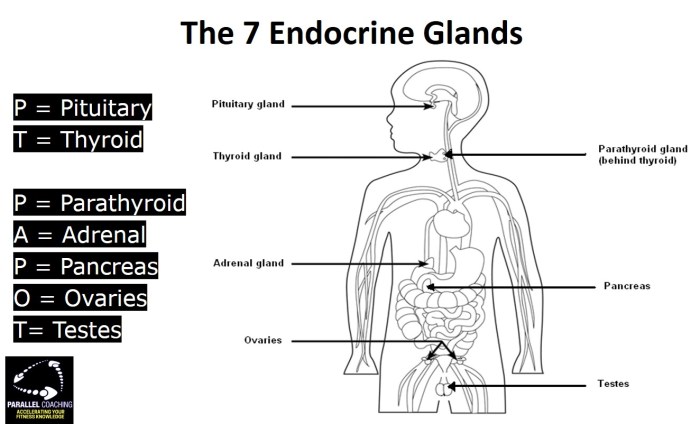
The major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries (in females) and testes (in males). Each gland produces specific hormones that have unique effects on target cells.
Mechanisms of Hormone Action
Hormones exert their effects on target cells through various mechanisms. Some hormones bind to receptors on the cell membrane, triggering a cascade of intracellular events. Others enter the cell and bind to receptors in the nucleus, directly regulating gene expression.
Regulation of Hormone Secretion
Hormone secretion is regulated by a complex interplay of factors, including feedback loops. Negative feedback loops ensure that hormone levels are maintained within a narrow range. For example, when hormone levels rise, the body releases hormones that inhibit further secretion.
Disorders of the Endocrine System
Disorders of the endocrine system can arise from hormone deficiencies or excesses. Common disorders include diabetes mellitus (insulin deficiency), thyroid disorders (abnormal thyroid hormone levels), and Cushing’s syndrome (excess cortisol).
Hormones and Disease
Hormones play a role in the development and progression of various diseases. For example, excess estrogen has been linked to breast cancer, while low testosterone levels can contribute to cardiovascular disease.
Therapeutic Uses of Hormones, Endocrine system hormones fill in handout
Hormones are used in medical treatments to correct hormonal imbalances. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat conditions such as menopause and hypothyroidism. Anabolic steroids are used to promote muscle growth in certain medical conditions.
Detailed FAQs
What are hormones?
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
How do hormones work?
Hormones bind to specific receptors on target cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately lead to the desired physiological response.
What are the different types of endocrine glands?
Major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries (in females) and testes (in males).
What are some common endocrine disorders?
Common endocrine disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders, and growth hormone deficiency.