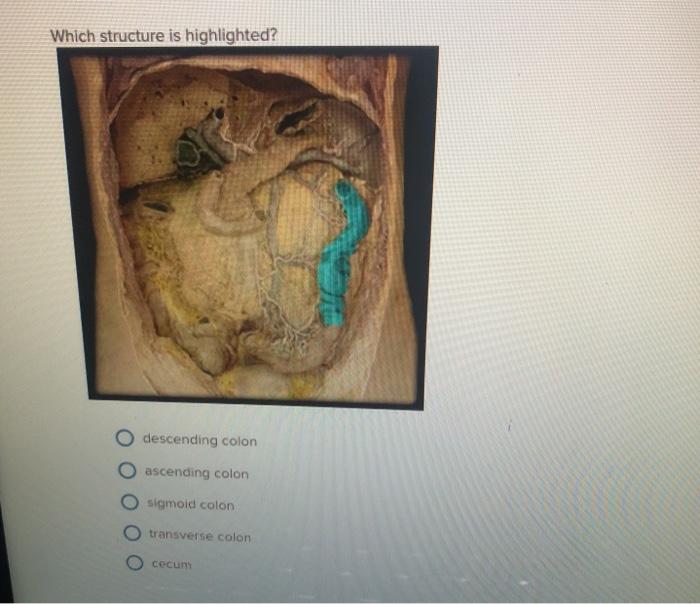
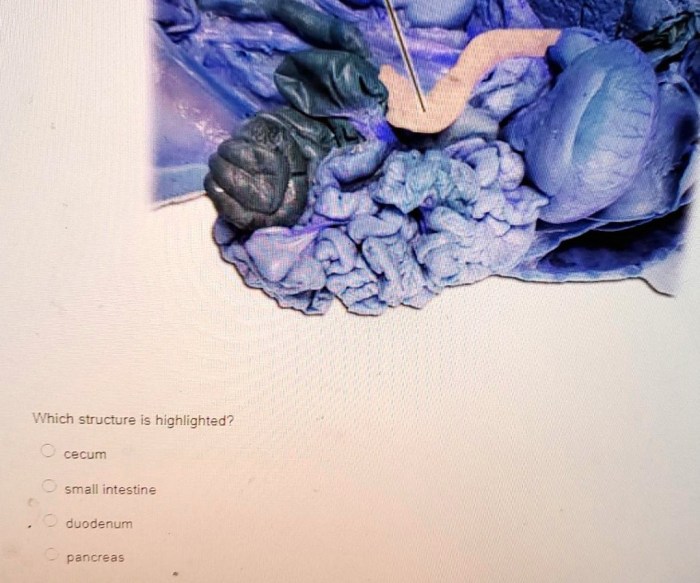
Which structure is highlighted cecum – The cecum, an integral component of the digestive system, stands out as a subject of immense interest. This article delves into the intricate structure and multifaceted functions of the cecum, shedding light on its histological features, comparative anatomy, clinical significance, and ongoing research frontiers.
Overview of the Cecum: Which Structure Is Highlighted Cecum
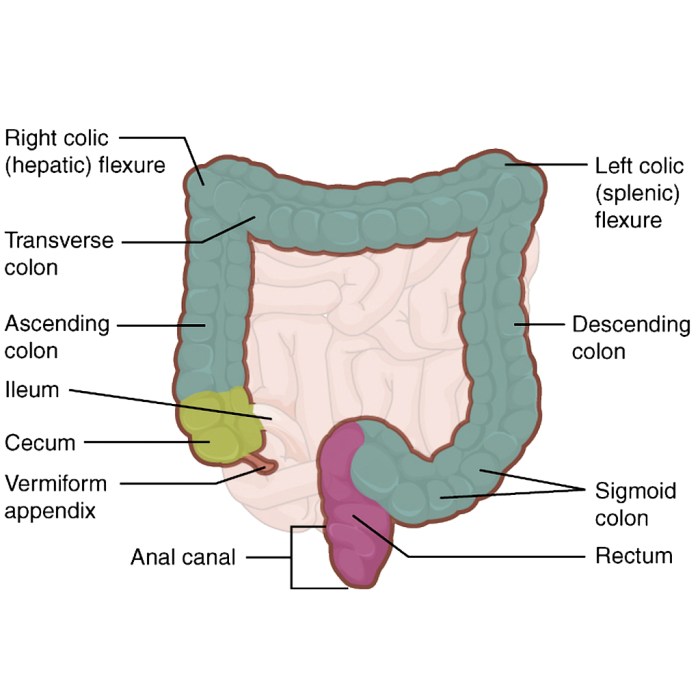
The cecum is a pouch-like structure located at the junction of the small and large intestines. It serves as a reservoir for undigested food and plays a vital role in the digestive process. The cecum is lined with specialized mucosa that contains crypts and villi, which increase the surface area for absorption and secretion.
Histological Features of the Cecum
The cecum consists of four histological layers:
- Mucosa: The innermost layer, composed of a simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells and crypts of Lieberkühn.
- Submucosa: A connective tissue layer containing blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
- Muscularis externa: A layer of smooth muscle that controls the movement of the cecum.
- Serosa: The outermost layer, a thin membrane that covers the cecum and attaches it to the surrounding structures.
Comparative Anatomy of the Cecum
The structure and function of the cecum vary among animal species. In herbivores, the cecum is typically larger and more complex, containing specialized microbial communities that aid in the digestion of cellulose. In carnivores, the cecum is smaller and less developed, reflecting their meat-based diet.
Clinical Significance of the Cecum, Which structure is highlighted cecum
The cecum plays a role in conditions such as:
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix, a small appendage attached to the cecum.
- Diverticular disease: The formation of pouches (diverticula) in the wall of the cecum, which can become infected or inflamed.
Research Frontiers in Cecum Biology
Current research focuses on:
- Understanding the role of the cecum in immune function and gut microbiota.
- Developing new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for cecum-related diseases.
- Investigating the potential of the cecum as a target for novel drug therapies.
FAQ Resource
What is the primary function of the cecum?
The cecum serves as a storage and fermentation chamber, facilitating the breakdown of ingested materials and absorption of nutrients.
How does the cecum’s histology contribute to its function?
The cecum’s histological layers, including the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa, provide structural support, facilitate nutrient absorption, and enable muscular contractions for mixing and propelling contents.
What are some clinical conditions associated with the cecum?
Appendicitis, diverticular disease, and cecal volvulus are among the clinical conditions that involve the cecum and can lead to inflammation, infection, or obstruction.