Hot plate vs bunsen burner – In the realm of heating devices, hot plates and Bunsen burners stand as two formidable contenders. As we delve into their contrasting designs, mechanisms, and applications, let’s unravel the intricacies that set them apart.
From the laboratory to the kitchen, these heating devices serve distinct purposes, each boasting unique advantages and considerations. Embark on this enlightening journey as we explore the nuances of hot plates versus Bunsen burners.
Definition and Overview

Hot plates and bunsen burners are both laboratory heating devices used in scientific research and educational settings. While they share the common purpose of providing heat for various applications, they differ in their designs, construction, and specific uses.
Hot plates are typically electric heating devices consisting of a flat, heated surface made of metal or ceramic. They provide a uniform and controlled heat distribution over the entire surface, making them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control and even heating.
Bunsen burners, on the other hand, are gas-powered devices that produce a concentrated flame through a metal tube. The flame can be adjusted to provide different temperatures and heat intensities, making them ideal for applications requiring localized heating or open flames.
Applications
Hot plates are commonly used in applications such as:
- Heating liquids and solutions in beakers, flasks, and test tubes
- Melting solids, such as wax or paraffin
- Evaporating liquids or drying samples
- Maintaining a constant temperature for reactions or experiments
Bunsen burners are typically used in applications such as:
- Heating glassware, such as test tubes or crucibles
- Sterilizing equipment or surfaces
- Providing a flame for combustion reactions or qualitative analysis
- Soldering or welding small metal pieces
Heating Mechanisms
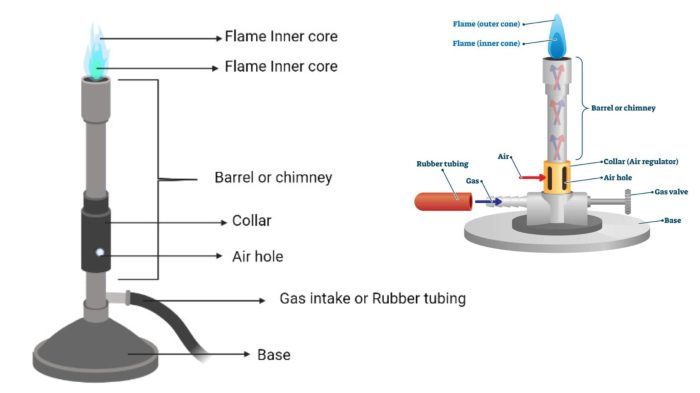
Hot plates and bunsen burners employ distinct heating mechanisms to generate heat for laboratory purposes. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for selecting the appropriate device for specific applications.
Hot Plates, Hot plate vs bunsen burner
Hot plates utilize an electrical resistance element, typically made of nichrome wire, which is embedded within a ceramic or metal plate. When an electric current passes through the resistance element, it generates heat due to its resistance. This heat is then transferred to the plate’s surface, which heats up and provides a consistent temperature for heating objects placed on it.
Bunsen Burners
Bunsen burners, on the other hand, rely on the combustion of a fuel, typically natural gas or propane, to generate heat. The fuel is mixed with air before combustion, resulting in a hot, luminous flame. The flame’s temperature can be adjusted by controlling the fuel and air mixture, providing a wide range of temperatures for various applications.
Temperature Control
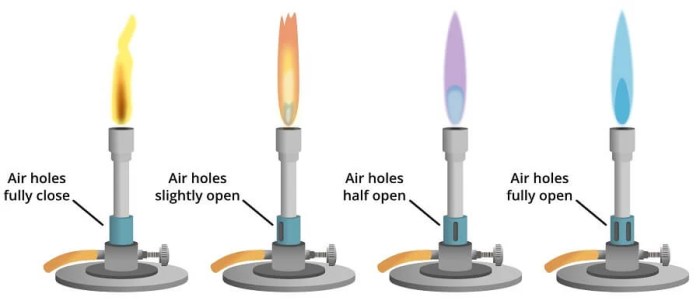
Controlling temperature is crucial in laboratory procedures involving hot plates and bunsen burners. Both devices offer different methods for adjusting and maintaining desired temperatures.
Hot Plates, Hot plate vs bunsen burner
Hot plates typically feature a built-in temperature controller that allows precise adjustment of the surface temperature. The controller may be a dial, knob, or digital display, providing a range of temperature settings. Some hot plates also have a thermocouple or other temperature sensor that monitors the surface temperature and adjusts the heating element accordingly, ensuring accurate and stable temperature control.
Bunsen Burners
Bunsen burners, on the other hand, do not have a built-in temperature controller. Instead, the temperature is regulated by adjusting the flow of gas and air. By adjusting the gas flow valve, the flame size and intensity can be controlled, which in turn affects the temperature of the flame.
When it comes to laboratory equipment, choosing between a hot plate and a bunsen burner can be a matter of preference and application. Hot plates provide a more precise and controlled heat source, while bunsen burners offer greater flexibility and portability.
For those seeking guidance on military drills and ceremonies, the drill and ceremony fm 22-5 provides comprehensive instructions. Returning to the topic of laboratory equipment, both hot plates and bunsen burners have their advantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the experiment.
Additionally, the air intake valve can be adjusted to mix air with the gas, which influences the flame’s temperature and characteristics.
Safety Considerations

Using hot plates and bunsen burners involves potential hazards, necessitating adherence to appropriate safety precautions. These precautions aim to prevent accidents, protect users from harm, and maintain a safe working environment.
Both devices emit heat, presenting risks of burns and fires. Additionally, bunsen burners utilize flammable gases, introducing further safety concerns.
Hot Plates, Hot plate vs bunsen burner
- Ensure a stable surface:Place the hot plate on a flat, stable surface to prevent spills or accidents.
- Avoid touching the hot surface:The hot plate’s surface can reach high temperatures, so use caution and avoid direct contact.
- Unplug when not in use:Always unplug the hot plate from the power source when not in use to prevent accidental activation.
- Keep away from flammable materials:Keep the hot plate away from flammable materials such as paper, cloth, or chemicals to avoid fire hazards.
- Allow cooling before moving:Let the hot plate cool down completely before moving it to prevent burns or damage.
Bunsen Burners
- Proper ventilation:Bunsen burners require adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of flammable gases.
- Leak detection:Check for gas leaks regularly using a soap solution. Bubbles indicate a leak, requiring immediate repair.
- Controlled ignition:Light the burner using a spark lighter or match, and adjust the gas flow to obtain a stable flame.
- Extinguish properly:Turn off the gas supply and allow the burner to cool before moving it to prevent accidental ignition.
- Handle with care:The burner’s metal parts can become hot during use, so handle it with caution to avoid burns.
Applications and Suitability

Hot plates and bunsen burners are commonly used in various laboratory and industrial settings. The choice between these heating devices depends on the specific requirements of the task at hand.
Factors to consider when selecting a heating device include:
- Temperature range
- Heat distribution
- Safety features
- Cost
Hot Plates, Hot plate vs bunsen burner
Hot plates are ideal for applications that require precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution. They are commonly used in:
- Chemical reactions
- Sample preparation
- Melting and boiling liquids
Bunsen Burners
Bunsen burners provide a focused, high-temperature flame. They are suitable for:
- Heating glassware
- Sterilization
- Flame tests
Advantages and Disadvantages: Hot Plate Vs Bunsen Burner
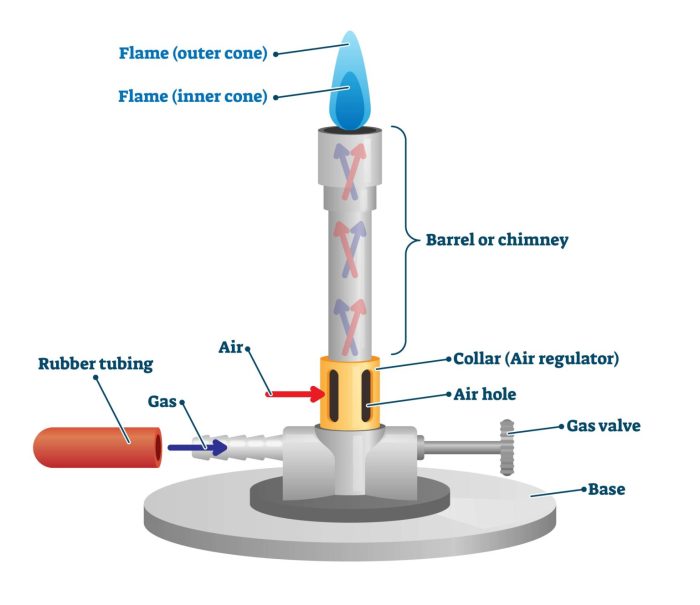
Hot plates and bunsen burners are both common laboratory heating devices, but they have different advantages and disadvantages.
Cost
- Hot plates are generally more expensive than bunsen burners.
- Bunsen burners are a more budget-friendly option.
Efficiency
- Hot plates are more efficient than bunsen burners because they transfer heat directly to the container.
- Bunsen burners lose some heat to the surrounding air.
Portability
- Bunsen burners are more portable than hot plates.
- Hot plates are not easily portable and require a power source.
Ease of Use
- Hot plates are easier to use than bunsen burners.
- Bunsen burners require some skill to operate safely.
Key Questions Answered
What is the primary difference between a hot plate and a Bunsen burner?
Hot plates utilize electrical resistance to generate heat, while Bunsen burners employ the combustion of fuel, typically natural gas or propane.
Which heating device offers more precise temperature control?
Hot plates generally provide more precise temperature control than Bunsen burners due to their integrated temperature sensors and electronic feedback systems.
Are there any safety concerns associated with using a Bunsen burner?
Yes, Bunsen burners produce an open flame, which poses potential fire and burn hazards. Proper ventilation and adherence to safety protocols are crucial.